These are the display codes that Ohio Edison is using:
4 = KWH delivered to customer
5 = Demand Delivered to customer
40 = KWH returned (customer generated and exported)
To calculate usage as well as power generated by solar panels, you only need to look at code 4 and code 40. To calculate your net power usage, just subtract the KWH code 40 displays from the KWH code 4 displays.
Here is an example:
KWH Delivered to Customer = Code 4 = 159 KWH
KWH Pushed to the Power Company = Code 40 = 108 KWH
The KWH the customer has used is the difference, or the net, which in this case would be 51 KWH.
Your monthly electric bill is calculated by taking the most recent KWH delivered reading (code 4) and subtracting last months KWH delivered reading (code 4). This result is called the KWH used for the month.
Next, take last months KWH delivered reading (code 40) and subtract that from the most recent KWH Delivered reading (code 40). This result is called the KWH Out.
Your monthly electric bill is then calculated by subtracting KWH out from KWH used.
Here is an example:
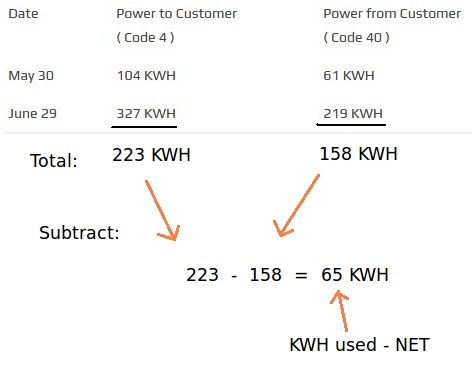
Calculate net meter monthly usage
By subtracting the two numbers in the Power to Customer column we get 223 KWH. On your Ohio Edison bill this is what they call KWH Used.
By subtracting the two numbers in the Power from Customer column we get 158 KWH. On your Ohio Edison bill this is what they call Kilowatt Hours Out.
The amount billed to you is calculated used these two numbers as shown below:
Amount billed =KWH used – KWH out = 223 – 158 = 65 Kilowatt Hours.
Something to be aware of with a net meter, if you have a separate monitoring system such as an Enphase Envoy for your solar panels, your net meter readings usually won’t agree. This is because the net meter does not read the power you generate and then use. It only records the excess power you have generated and sent back to the utility.
This article was originally posted on www.mikestechblog.com Any reproduction on any other site is prohibited and a violation of copyright laws.
My Solar Edge app seems to indicate that my solar panels are producing more kilowatts than what my local electric company is giving me credit for. What might be the best way to resolve this apparent discrepancy with my local company.
That is typical and I have the same issue.